如何使用“圈养”保险来减轻气候变化风险

This article is the second in a three-story series culled from theMMC Climate Resilience 2018 Handbook (PDF)并最初在边缘出版。可能会发现一部分专注于气候适应的绿色债券策略here.
这effects of climate change are increasingly exposing businesses to new and unpredictable risks; often they can be catastrophic in nature or interfere with an organization's ability to do business, which inherently drives up the associated operational costs.
这全球风险报告2018revealed that over the past decade, extreme weather events and failure of climate change mitigation and adaptation, as well as water crises, consistently have emerged as key risk concerns to business leaders in the global risk landscape. These risks are interconnected and can exacerbate many other risks, such as domestic and regional conflict as well as involuntary migration. According to the report, every environmental risk that was assessed has become more prominent, each rising above the average on both scales of likelihood and impact.
Organizations can capture major strategic advantages by quantifying these risk factors and using traditional risk transfer and captive use along with reinsurance, where appropriate. (See Exhibit 1.)
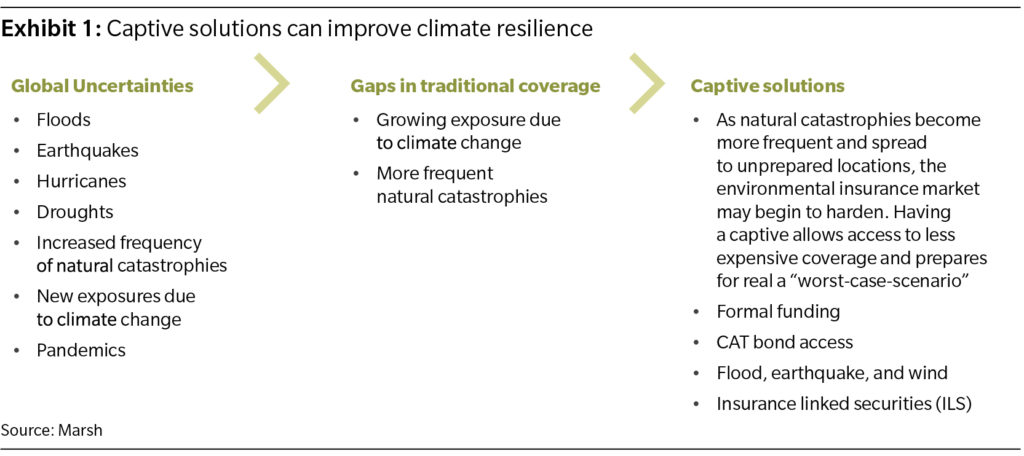
寻求新的解决方案
尽管联合国气候变化会议的影响以及一系列控制石油,污染和其他因素的新法规,但在许多情况下,国际业务面临的环境问题和损害尚未立即解决。一些企业已经感觉到气候变化驱动因素(例如污染)的影响。
A prime example is the hazardous smog blanketing several of China's larger cities. This issue has caused metropolitan areas such as Beijing to shut down businesses for days until the pollution and haze dissipates. These events may lead to contingent business interruption losses, which may be insurable. However, such events may be difficult to insure on the commercial markets, unlike other climate-related risks that result in physical property damage. So, with very limited options, companies are creating their own insurance solutions in captive insurance companies.
什么是圈养保险公司?
A captive insurance company is a bona fide licensed insurance or reinsurance company owned by a non-insurance company, which insures or reinsures the risks of its parent or affiliated companies. Simply put, it is a formalized mechanism to finance self-insured risks or access the reinsurance market.
从历史上看,大多数俘虏是由北美和欧洲的母公司组成的,但新趋势开始出现。在过去的三年中,沼泽(Marsh)看到了受俘虏所有者驱动的新兴地理的兴趣日益增长整个欧盟。与上一年相比,拉丁美洲母公司成立的俘虏在2016年增长了11%,使其成为俘虏增长最快的地区。
许多人认为俘虏只会写传统或可预测的风险;但是,这不是真的。Organizations can capture major strategic advantages by quantifying these risk factors and using traditional risk transfer and captive use along with reinsurance, where appropriate.
Captives can write high-severity, low-frequency risks as well. As insurance companies, they are able to access reinsurance markets and alternative capital markets to fund less predictable retained risks that are uninsurable or difficult to insure on the commercial market. Furthermore, a captive can act as a risk-financing vehicle that, over time, builds up surplus to pay for more catastrophic risks such as hurricanes and earthquakes. This helps organizations reduce cash flow volatility and decrease budget uncertainty.
How to use captives for climate risks
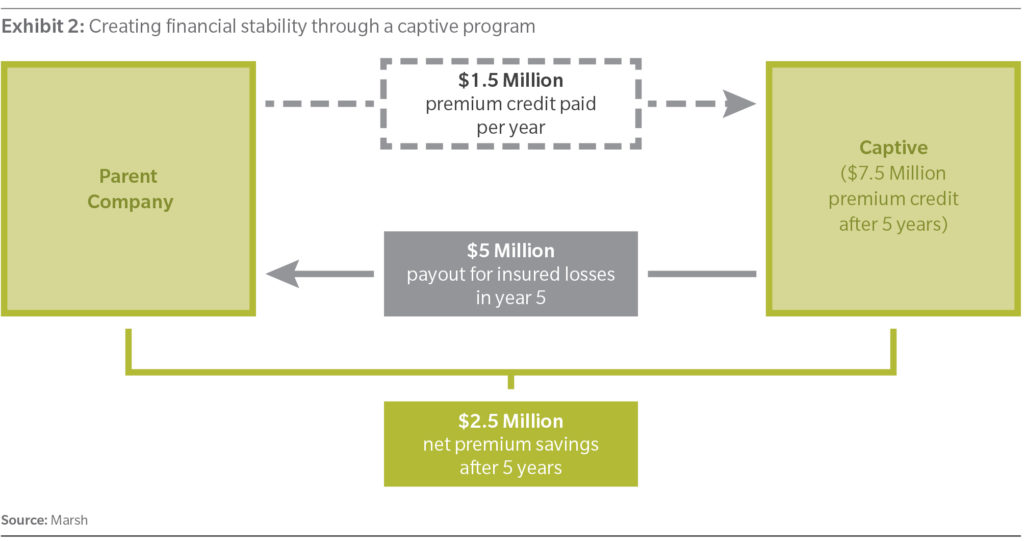
For example, consider an organization that has a large property exposure with an existing $1 million deductible. It could determine that it can raise its deductible to $2 million and receive a $1.5 million premium credit. The company has not had any product liability losses in excess of $1 million in the past 10 years, so it decides to assume the higher deductible of $2 million. It then decides to remit the $1.5 million premium savings into a captive, which will insure the $1 million excess/$1 million layer.
As illustrated in Exhibit 2, the company recouped $2.5 million in net premium savings over five years by obtaining capacity from the captive instead of the commercial insurance market. In addition, by formally putting aside premiums into the captive each year, the parent had proper reserves accrued, which ultimately stabilizes earnings for the consolidated organization.
Captives可以通过提供可定制的覆盖范围并提供访问其他难以确保损失的车辆来为极度不确定的环境景观提供安全性。例如,与风能和公用事业公司的传输和分销线相关的损失以及影响。
最近,俘虏显示供应链风险的吸收率很高(从2014年到2015年,沼泽管理的俘虏增长了133%)。被认为是非专业损害业务中断,这种风险可能是全球天气事件引起的,最终可能影响全球一半的业务。例子包括2011年的泰国洪水,2011年的日本地震和海啸以及2017年的哈维飓风。
Protecting your business from rising supply-chain risk
这combination of climate change, global financial pressures and political protectionism demonstrates the critical importance of global supply chains and the potential impact of their failure.
鉴于当今高度不确定的商业环境,公司可能会寻找俘虏,以提供更全面的供应链覆盖范围。传统的业务中断保险仅提供有限的保护,因为它仅限于(主要是)一级供应商的身体损失或损害的影响。由俘虏资助的预先定位风险评估支持的全风险供应链覆盖物的发展可以为组织中的组织中的组织提供额外的舒适感。
It is important that risk managers work closely with their own supply-chain managers and external advisers where appropriate in order to:
- 识别/验证关键的商品和服务供应商以及他们所依赖的供应商。
- 评估和量化该供应损失及其固有的弹性的影响。
- Obtain indicative costs for all-risks supply‑chain cover for key elements.
- 考虑通过圈养车辆的初步评估资金和风险转移。
这assessment of supply-chain risk is not, however, a stand-alone exercise, but one that should form part of an integrated approach to the identification, mitigation and transfer of risk. Climate change is having an immediate effect on global business operations through massive property loss and business interruption.
许多俘虏的父母和准圈养所有者应考虑写作财产,风,洪水,业务中断以及供应链的覆盖范围的好处,以防止这些日益增长的环境威胁。
This story first appeared on: